Level of Protection
Protection Class: Standardized Protection for Perfect Operation Safety
For safe handling of electric components of all sorts devices, parts and components are split into protection classes. The standard of this protection class is found in EN 61140 and VDE 1040-1. The goal of the standard is to create design specifications in a way that components are safe to handle.
Protection Class or Type of Protection
When classifying electric devices with a network connection a distinction has to be made in between "protection class" and the "type of protection". The "protection class" defines measures on how to set up a device so it can not cause an electrical breakdown. "Types of protection" specifically the "IP (Ingress Protection according to IEC 60529) types of protection" classify the type of stress put on the case. In the definition of the IP classes measures in regards to the case design can be found to protect it against water and other foreign objects.
Protection Class 0
Even though four protection classes are defined in regards to electric components within the EU only classes 1-3 are officially used. "Protection Class 0" describes electric devices with a network connection which have no additional protection in addition to the basic isolation. There is no official approval for devices with "protection class 0" in Germany and Austria. Devices belonging to this class can be recognized by the lack of a mark regarding the classification.
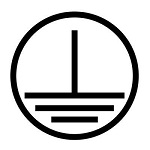
Protection Class I
A device with the classification protection class I has the following features:
- All conductive case parts have a ground
- Moving devicess ahne a plug connection with a protective ground contact
- When plugging in a connector the ground is connected first and when removing it is unplugged last.
- The FI switch has to be triggered by errors caused by a protective conductor touching the case. With in milli seconds the circuit is completely switched off and free of any voltage.
This protection class does not have an own symbol as indicator. It is marked by a ground symbol. Devices of protection class 1 can be visibly recognized by a safety plug.
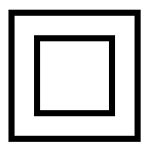
Protection Class II
Devices belonging to protection class II have a double or strengthened insulation. Characteristics of such devices is:
- Plastic Case
- Either a flat Euro Style Plug or a Counter Plug
Both types of plug do not have a protective contact. Devices with a metal case may also be included in protection las II as long as the electric components inside are sufficiently shielded. The maximum amount of leakage current the in this case may not exceed 0,5 mA. The symbol of protection class II are two squares arranged inside each other. They symbolize the double insulation. The type of insulation of devices belonging to this protection class is defined in the standard VDE 0100 part 410.
Protection Class III
Protection class III is meant for devices equipped with safety extra low voltage or protective low voltage. This includes all devices powered by a battery. These devices must only be connected to SELV/PELV (low voltage up to 50V AC / 120V DC) voltage sources.
These include: Safety transformers, rechargable batteries or low voltage generators.
Regardless of the low operating voltage PELV power sources have to be equipped with a stronger or double insulation. This insulation is not required as a measure against voltage punctures but for radio interference suppression.
When is Protection Class 1 used?
Protection class 1 is the standard for bigger electric devices. Especially devices creating a higher voltage are better secured by it. Higher voltages are required to power electric engines or heating coils. Floor mounted appliances are often included into this class:
- Refrigerators
- Electric Stoves
- Washing Machines and Dryers
Refrigerators contain a compressor which is power by an electric engine. High voltages are required to power this engine. In addition a refrigerator attracts humidity. Therefore a special type of shielding is required.
Electric stoves contain a stiff coil made from a chic metal wire. These create a high resistance for the current which can only be overcome with a high voltage.
Devices producing heat such as irons, drills or water heaters are also included in protection class 1.
Protection class 1 offers the highest level of protection of all classes. The shield of these devices is set up redundant or double. The primary insulation of the devices is reached by a special type of insulation of cables and cases. In addition all electric conductors in the device have a ground. If direct or indirect conduct occurs in between an electric conductor and a live component the voltage is grounded via the protection contact line. The technical term for this process is "equipotential bonding". Protection class 1 devices can be recognized by their plug. They completely fill out the socket. In addition they have a reed on the top as well as the bottom. Those are intended for the protection contact.
When is Protection Class 2 used?
Protection class 2 is intended for devices which do not create a high voltage and therefore are not part of protection class 1. Nevertheless protection class 2 devices could still use high voltages which may present a danger when not working correctly. Therefore protection class 2 devices have an especially strong insulation. In contrast to protection class 1 they do not have the ability of equipotential bonding.
Common protection class 2 devices are:
- Power Tools with a Cable
- Lamps
- Blow Dryers and Epilators
Protection class 2 devices have an especially strong insulation between the circuit and the output voltage. This insulation shields all parts which may be touched safely. The case and the switch are in most cases made of non conductive plastic. In protection class 2 the case is not viewed as an insulation in accordance to protection class 2. Therefore it is possible to make a protection class 2 device with a metal case. The actual insulation or shield for the network voltage is mounted inside the device. Especially strong shielded cables and insulated conductors make up this insulation. Protection class 2 devices can be recognized by their plug. They look similar to the plugs of protection class 1 but are missing the reeds for equipotential bonding.
When is protection class 3 used?
Protection class 3 is also known as "safety extra low voltage". It is used for devices which are run by a low voltage supply. In most cases they can be recognized by a flat plug. Typical devices of protection class 3 are:
- Radio Alarms or Portable Radios
- Toys
- Chargers
- Small Appliances like a Hand Mixer or an Ultrasound Cleaner
- Small Devices for Sanitary Areas (Electric Razors)
The maximum voltage tolerated for protection class 3 devices is 50 Volts AC or 120 Volts DC. Both voltage ranges are harmless for humans when getting into contact. Therefore the set up of protection class 3 devices is especially safe and a simple additional insulation is sufficient. The disadvantage is they only offer a limited amount of power.
Protection class 0 devices are not available in Germany.